Diabetes is a chronic condition that results in complications affecting the cardiovascular system, nervous system, kidneys, eyes, immune system and digestive system.
Diabetes is a condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the body either does not produce enough insulin or cannot effectively use the insulin it produces. Insulin is a hormone crucial for regulating blood sugar (glucose) levels and when this balance is disrupted, it can lead to various complications. In this article we will explore the impact of diabetes on the body and how it can affect different organs and systems of human body.
Blood Sugar Regulation

The primary role of insulin is to help cells absorb glucose from the bloodstream for energy. when you eat, the concentration of glucose in your blood rises. When it goes too high then pancreas releases insulin into the bloodstream. This insulin stimulates the liver to convert the blood glucose into glycogen for storage. If the blood sugar goes too low, the pancreas release glucagon which causes the liver to turn stored glycogen back into glucose and release it into the blood. In diabetes, this process is compromised which leads to elevated blood sugar levels (hyperglycemia). Persistent hyperglycemia can damage blood vessels and nerves throughout the body and contribute to various complications.
Cardiovascular System

Diabetes significantly increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases. High blood sugar damages blood vessels through a process known as glycation. Elevated glucose levels in the bloodstream can bind to proteins and form harmful molecules that accumulate on blood vessel walls. This leads to inflammation, oxidative stress and the thickening and narrowing of blood vessels. This condition known as atherosclerosis. This condition restricts blood flow and increases the risk of heart attacks and strokes. Additionally, diabetes can contribute to high blood pressure and abnormal lipid profiles causing further escalated cardiovascular risks.
Nervous System

Neuropathy or nerve damage is a common complication of diabetes. High blood sugar level can injure the blood vessels supplying the peripheral nerves, irritating and damaging them in the process. Such accumulated nerve damage is called diabetic neuropathy. It can affect any part of the nervous system causing symptoms such as tingling, numbness and pain often starting in the extremities. Peripheral neuropathy can lead to complications like foot ulcers and infections, which may be challenging to heal due to reduced sensation and impaired circulation.
Kidneys

Diabetes is a leading cause of kidney disease known as diabetic nephropathy. Diabetic nephropathy is a kidney disease resulting from prolonged diabetes which is characterized by damage to the kidney’s filtering units. High level of blood sugar can damage the tiny blood vessels in the kidneys, impairing their ability to filter waste and excess fluids from the body. This can result in kidney failure over time which require dialysis or transplantation.
Eyes

Diabetic retinopathy is a condition that affects the eyes and is a leading cause of blindness in adults. It is a serious sight-threatening complication caused by high blood sugar. Over time, diabetes damages small blood vessels throughout the body including retina. Diabetic retinopathy occurs when these tiny blood vessels leak blood and other fluids. This causes the retinal tissue to swell which causes cloudy or blurred vision.
Immune System
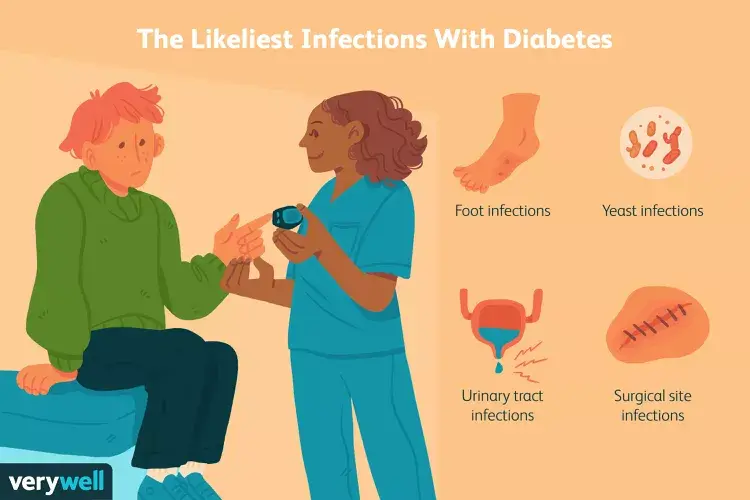
People with diabetes may have a weakened immune system, making them more susceptible to develop infections. In addition, some diabetes related health issues such as nerve damage and reduced blood flow to the extremities result in increased body vulnerability to infections like Foot infection, Yeast infection, Urinary tract infection and surgical site infection etc. Poorly controlled diabetes can impair the body’s ability to fight off pathogens which leads to frequent infections and slower healing of wounds.
Digestive System
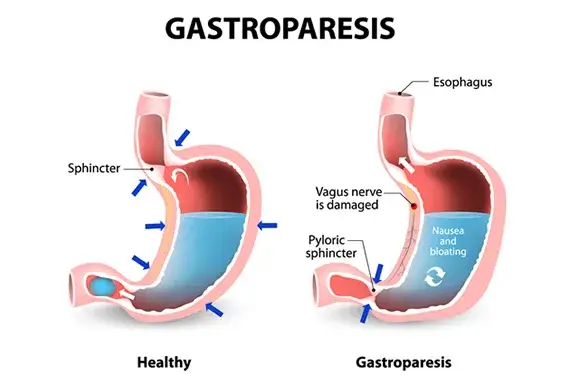
Diabetes can affect the digestive system and cause complications such as gastroparesis. Gastroparesis is a condition where the stomach is unable to empty food normally. Normally, the muscles in the digestive system use contractions to move the food along but with gastroparesis, damaged muscles and vagus nerve that control the movement can’t function correctly. This can result in symptoms like nausea, vomiting, heart burn and problems with blood sugar control.
Conclusion
Managing diabetes effectively through lifestyle changes, medication and regular medical monitoring is crucial to prevent or mitigate these complications. Understanding the impact of diabetes on the body highlights the importance of early diagnosis, proactive management and ongoing support for individuals living with this chronic condition. By knowing the underlying factors contributing to diabetes and its complications and with timely treatment, one can lead healthier life and reduce the risk of long term damage to various organs and systems in the body.
For more related content click here

