Trees are often celebrated as nature’s guardians, vital for maintaining ecological balance and sustaining life on Earth.
Beyond their aesthetic beauty and ecological significance, trees play a crucial role in mitigating climate change, particularly in combating global warming. Understanding how forest interact with the Earth’s climate system is essential for devising effective strategies to address climate change. In this article, we delve into the multifaceted relationship between trees and global warming.
The Carbon Cycle
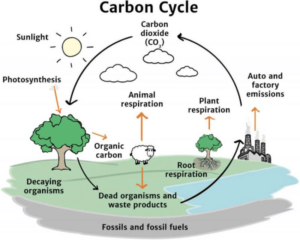
At the heart of the tree-global warming relationship lies the carbon cycle. Trees are remarkable carbon sinks, absorbing carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere during photosynthesis and converting it into organic matter. Through this process, trees sequester carbon, storing it in their biomass and in the soil. This carbon storage function is pivotal in regulating atmospheric CO2 levels, thus mitigating the greenhouse effect and reducing global warming.
Albedo Effect

Trees also influence global warming through the albedo effect. The presence of tree canopies alters the Earth’s surface reflectivity or albedo, by absorbing solar radiation. This absorption contributes to local warming but can also have a cooling effect by shading surfaces and reducing the amount of solar energy absorbed by the ground. The net effect depends on factors such as density, leaf structure and geographic location.
Forest Ecosystem Services

Forests provide a myriad of ecosystem services that indirectly influence global warming. They regulate regional climates by moderating temperature extremes, influencing rainfall patterns and stabilizing soil moisture levels. Additionally, forests support biodiversity, which enhances ecosystem resilience to climate change. Protecting and restoring forest ecosystems is therefore essential for maintaining these vital services and mitigating global warming.
Deforestation & Land Use Change

Conversely, deforestation and land use change contribute significantly to global warming. When trees are cleared for agriculture, urbanization or other purposes the carbon stored in their biomass is released back into the atmosphere as CO2. This process not only diminishes the carbon sequestration capacity of forests but also reduces their albedo effect, further exacerbating global warming. Addressing deforestation and promoting sustainable land management practices are critical components of climate change mitigation efforts.
Reforestation and Afforestation

Reforestation and afforestation initiatives are key strategies for harnessing the climate mitigation potential of trees. By planting trees on degraded lands or restoring deforested areas, we can enhance carbon sequestration, restore ecosystem services and contribute to climate resilience. These initiatives not only help combat global warming but also provide additional benefits such as habitat restoration, watershed protection and economic opportunities for local communities.
Conclusion
Trees are indispensable allies in the fight against global warming. Their role as carbon sinks, influencers of the albedo effect, providers of ecosystem services and targets for conservation and restoration underscores their importance in climate change mitigation strategies. By recognizing and harnessing the power of trees, we can work towards a more sustainable and resilient future for our planet.
For more related content click here.

